LEED AP CERTIFICATION EXPLAINED!
WHAT IS LEED AP AND HOW TO PASS THE LEED AP BD+C EXAM IN 2 WEEKS

TRUSTED BY 5,000+ STUDENTS
TRUSTED BY 5,000+ STUDENTS

WHAT IS LEED AP
LEED AP stands for LEED Accredited Professional. For those who are wondering about LEED AP meaning, it refers to a professional who has advanced knowledge of the LEED rating systems and plays an important role in directing project teams toward sustainable, low-impact constructions.
Just as developers advertise their buildings as LEED certified projects to gain tax incentives, sell the projects faster and for more. Architecture and Engineering firms are leveraging the number of LEED AP employees. Which helps secure more projects and stand out from competition, showcasing credibility, knowledge and authority in green building practices.
Among the LEED specialties, the demand for LEED AP BD+C is highest. Simply due to more LEED BD+C projects. Most LEED projects are new construction and major renovation, which requires LEED AP BD+C professionals.
+5,000 OF OUR STUDENTS PASSED THE LEED AP test, it’s your time!



meet your instructor

shadi abousamra
LEED TRAINER, SUSTAINABILITY CONSULTANT, UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR
Shadi AbouSamra is a Sustainability consultant, LEED and WELL AP trainer, and university professor. Specialized in sustainable design, LEED certification, and high-performance buildings.
He has trained over +5,000 professionals to pass the LEED AP test and WELL AP.
Students worldwide have been prepared by Shadi from USA, UAE, Canada, KSA and many more.
His LEED test preparation has saved professionals their valuable time and money. Helping scale their career and become more credible, using live and on-demand LEED AP courses that has achieved a 100% pass rate.
















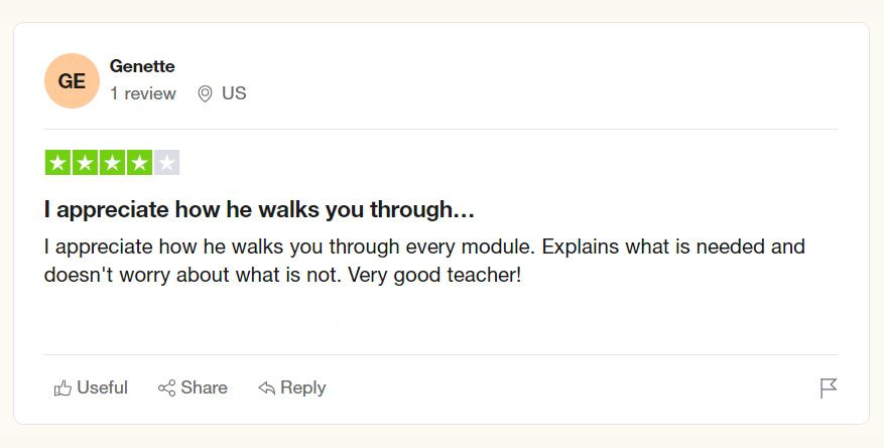
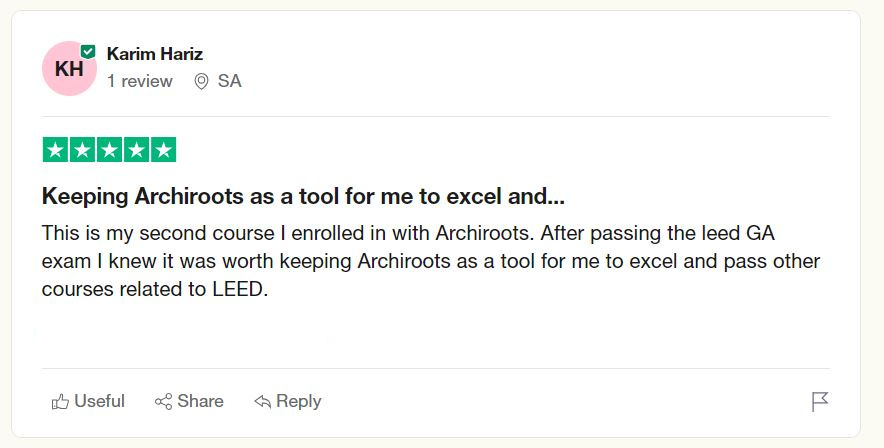
IS THE LEED CERTIFICATION WORTH IT? SEE WHAT OUR STUDENTS ARE SAYING
- 35% SALARY HIKE
- Ashraf Shaaban
Project Manager
- 50% SALARY HIKE
- Omar Doughan
Operations Manager
- 47% SALARY HIKE
- Zeina Sawaya
Arch. Consultant
- FIRST JOB
- Linda K.
Junior Architect
- 20% SALARY HIKE
- Daria Taeb
Project Manager
- Ashraf Shaaban
Project Manager
- Omar Doughan
Operations Manager
- Zeina Sawaya
Arch. Consultant








LEED AP CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS
To be eligible for the LEED AP certification there are mainly two LEED certification requirements set by USGBC and GBCI.
1. Hold a Valid LEED Green Associate Credential
It is crucial to have passed the LEED Green Associate exam before taking the LEED AP exam. It is also important to maintain the credential by satisfying the LEED CE hours, since expired credentials will force the candidate to retake the Green Associate exam.
Candidates also have the possibility to take a 4 hour combined LEED Green Associate and LEED AP exam in one sitting rather than 2 exams of 2 hours each.
2. To be 18 Years Old
All applicants must be at least 18 years old when they register for the LEED test. In order to guarantee professional and legal preparedness for the certification, this is a fundamental prerequisite.
LEED AP BD+C
The LEED AP BD+C is the most in-demand LEED accreditation today. Since most LEED projects are being certified under the BD+C rating system which stands for Building Design and Construction.
The LEED AP BD+C is for professionals looking to become credible in the building industry with a specialty under new construction and major renovation LEED projects.
This LEED professional certification has proven to increase salaries, support companies in landing more projects and streamlining the certification process. Becoming a LEED accredited professional will most likely help your resume stand out from competition and showcase knowledge about the LEED certification and green buildings.

BECOME A LEED AP BD+C!
