As sustainability becomes a central concern of the architectural industry, energy analysis software for architects has become a key factor using sophisticated digital technology more and more to design structures that satisfy strict energy and daylighting criteria. Projects aiming for a green building or certifying it under strict criteria’s like the LEED certification, depend on sustainable building design software that help to earn points for occupant comfort, daylighting, and energy efficiency, thereby influencing the design of sustainable buildings.
To help architects include sustainable practices into their designs, this short read looks at the 6 most used design for sustainability software. Includes efficient building design software, climate analysis, energy modeling as well as their support to LEED projects.
What is an Energy Modeling Software?
In response to rapid urbanization and environmental issues, architect designing have emphasized sustainable building design. Architects who are building ecologically friendly buildings are becoming more dependent on advanced sustainable design software technology to put their ideas into action and in order to meet strict sustainability criteria.
These software include lighting analysis, energy modeling, ray tracing and many more. Which are critical to meet aesthetic and functional criteria while significantly lowering negative environmental impact. Architects may effortlessly combine environmentally responsible principles such as enhancing the inclusion of natural daylight light and regulating energy usage.
This alteration complies with green building standards and helps project earn LEED and WELL certifications, which recognize sustainability-focused innovations, enhanced interior environments, and energy efficiency. The increased requirement for accuracy in meeting green building standards reflects the demand for such software. Integrating data-driven insights with creativity, notably in the areas of indoor environmental quality and energy efficiency.
Energy modeling software helps architects optimize elements such as thermal comfort, daylight autonomy, and shadow influence by using equipment particularly designed for sustainable architecture. Advanced energy modeling may help uncover ways to minimize heating, cooling, and lighting needs, while daylight analysis methods improve natural light penetration while preserving thermal efficiency.
Benefits of Sustainable Design Software
More than merely being more effective, sustainable design software is revolutionizing the way architects design structures. Such technologies provide architects with precise tools to reduce a project’s carbon footprint while increasing a building’s energy efficiency, maximizing natural light, and controlling HVAC loads.
By allowing you to examine a building’s energy use, natural light intake, and indoor air quality, these software solutions facilitate meeting the stringent green standards. Sustainability has always been a challenging and costly objective. However, it is now a simple and achievable norm thanks to contemporary sustainable construction techniques.
Apart from obtaining LEED or similar, architect designing software enables to create environments that improve people’s health and reduce the building’s long-term operating expenses. For instance, designers may include daylight and solar gain to reduce heating, thanks to technology that simulate daylight autonomy.
In order to strike a balance between sustainability and aesthetics, energy modeling tools also provide architects with information on how to enhance insulation and reduce the demand for HVAC systems. These technologies are becoming more and more crucial for architectural companies that want to satisfy customer demands for affordable, environmentally friendly structures as the need for green buildings increases.
6 Best Energy Analysis Software For Architects
1. Energy Analysis with Revit and Insight
The most notable feature of Revit is its Building Information Modeling (BIM) feature, which allows architects produce intricate models combining analytical and design aspects. Its features include vast materials library, real-time energy evaluation, and daylight simulation which significantly improve the possibility for sustainable design.
Architects may evaluate a building’s energy performance at the initial phases of the design process using such advanced energy analysis software by combining the program with Insight. This application enables design teams to make informed choices improving energy efficiency and guaranteeing adherence to LEED criteria.
One notable project is the Seattle Bullitt Center made extensive use of Revit for energy modeling and analysis. Built to generate an equal volume of energy to its yearly use, the Bullitt Center achieves net-zero energy use. To reach this ambitious target, the design team relied mostly on Revit as a tool for energy modeling.
Using Revit design software for architecture, to produce accurate 3D models of the building throughout the design process including sustainable elements like solar panels, high-performance insulation, and effective HVAC systems. The way the program interacted with Insight helped the team to undertake real-time energy analysis. This allowed them to change their designs in line with the simulated energy consumption of the building under certain design criteria.
The architects ran several simulations to evaluate how various building orientations and materials affect energy performance. This study showed how overhangs and window glazing may maximize daylight while limiting heat absorption, therefore lowering the need on artificial lighting and air conditioning.
Designed in Revit to guarantee effective water management, the rainwater collecting system enhances the environmental credentials of the Bullitt Center. Using Revit’s extensive analytical tools, the design team made sure that every element of the building improved its overall energy efficiency, therefore attaining LEED Platinum certification and Living Building Challenge.
2. Ladybug and Honeybee ( on Rhino and Grasshopper )
Ladybug and Honeybee are famously known for climate analysis software for architecture to conduct complex simulations. They are mere plugins that work on Grasshopper, which is a software that runs on another software that acts as the engine which is Rhino. Grasshopper is known for paramteric architecture and Rhino is known for helping designers generate organic projects.
These efficient building design software allow variety of environmental factors, including daylight simulation, solar radiation, ray tracing, shadow analysis and energy consumption. In order to optimize daylight, mitigate pollution, and reduce energy costs.
One prominent example that has used these tools is the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, Sweden. A noteworthy project that is utilizing Ladybug for daylight autonomous simulation. The design team employed Ladybug to assess the building’s orientation, window dimensions, and shading systems in order to ensure that the interior spaces receive an adequate amount of natural light and to reduce pollution. The architects sought to achieve a spatial daylight autonomy (sDA) of 300 lumens or higher and determined the areas of the building that would profit the most from direct sunlight by simulating daylight autonomy.
The design process was informed by this analysis, which led to the optimization of window placements and overhangs to ensure optimal daylight infiltration. The outcome was a learning environment that promoted comfort and motivation among students and instructors, while simultaneously reducing dependence on artificial lighting to improve energy efficiency.
3. IES VE (Virtual Environment)
IES VE is a sophisticated design for sustainability software that generates mature statistics about the HVAC loads. A bit more advanced than daylight simulating softwares like Ladybug. IES VE is recognized for its comprehensive energy modeling capabilities which allows architects and engineers to evaluate a variety of energy optimization solutions and simulate HVAC loads, thereby offering critical insights that are consistent with LEED credits for energy efficiency.
This software for architecture enables users to develop exhaustive energy simulation models that assess the impact of various design decisions on a building’s overall energy efficiency. The program is a critical resource for sustainable design, as it offers comprehensive analytical tools that optimize building systems, materials, and configurations to reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency.
The Sustainable Office Building in Chicago is a prime example of a project that effectively implemented IES VE for energy modeling. The consulting firm Cyclone Energy Group, which is in charge of the project, has used the IESVE program a lot to look at and improve the energy economy of complex high-rise buildings. The design team utilized IES VE to perform precise simulations of HVAC loads and energy consumption, with an emphasis on the ways in which specific design features enhanced the building’s overall energy efficiency.
By simulating a variety of scenarios, including the effects of high-performance windows, efficient insulation, and modern HVAC systems, the researchers was able to identify optimal designs that significantly reduced energy consumption. The project obtained numerous LEED credits for energy optimization as a result of modeling findings that suggested a decrease in annual HVAC loads. This initiative emphasized the significance of data-driven design choices in the pursuit of sustainability objectives and demonstrated the efficacy of IES VE in modeling energy performance.
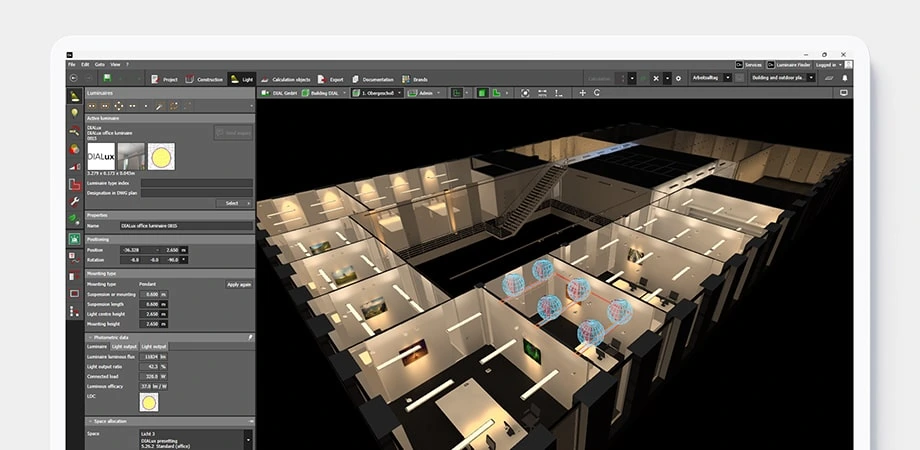
4. Dialux
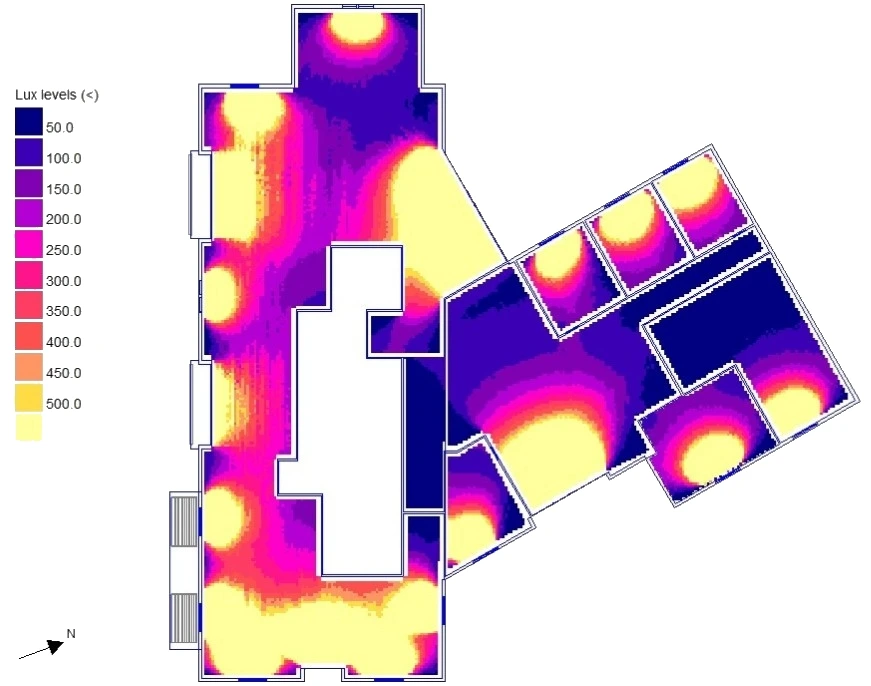
Dialux is a comprehensive lighting analysis tool capable of accurately simulating sunlight. Dialux is considered one of the best energy analysis software for architects for it’s easy modeling to achieve LEED daylighting credits, ensuring sufficient natural illumination in spaces and minimizing reliance on artificial lighting. This tool accurately forecasts daylight conditions, so facilitating the assessment of optimal window placement and dimensions to enhance energy efficiency in structures.
The Green Learning Center project demonstrates the use of Dialux for collecting solar exposure data. The project sought to get LEED Daylight credit by simulating access to natural light. The team optimized window space and used interior materials that reflect light, so demonstrating using Dialux that natural light satisfied the majority of daily lighting requirements. This method enhanced the building’s LEED certification score in daylighting, so augmenting its environmental sustainability and diminishing reliance on artificial lighting.
5. Energy Evaluation with ArchiCAD
As a powerful BIM software for architect design, ArchiCAD is widely used for energy assessments as well. A design for sustainability software that supports Architects with daylighting visualize with ArchiCAD’s daylight simulation tool, which contribute to sustainable design goals. In order to make buildings more efficient and reduce their energy usage, the initiative backs the use of energy modeling tools.
Designers may easily determine a building’s energy efficiency within the BIM model with ArchiCAD’s energy evaluation feature. It has tools for calculating energy use, modeling HVAC needs, and exploring different design options for more efficient use of energy. This inquiry is essential since following LEED standards relies on architects making well-informed judgments about building orientation and material selection.
6. TAS ( Thermal Analysis Software )
TAS, designed to look at building performance in terms of temperature control, air conditioning loads, and overall energy use, this comprehensive energy modeling software for architects and engineers reproduce several scenarios to meet LEED standards, BREEAM and optimize energy efficiency.
Such dynamic energy modeling simulations showcase thermal comfort and HVAC systems as well that proves a project’s energy performance and can then earn points on standards.
8 Energy Modeling & Daylight Simulation Examples
Here’s a breakdown of the essential simulations architects use in sustainability-focused design, particularly for LEED and WELL certification. Each section includes an overview of the simulation, how it supports sustainable architecture, and relevant LEED credits.
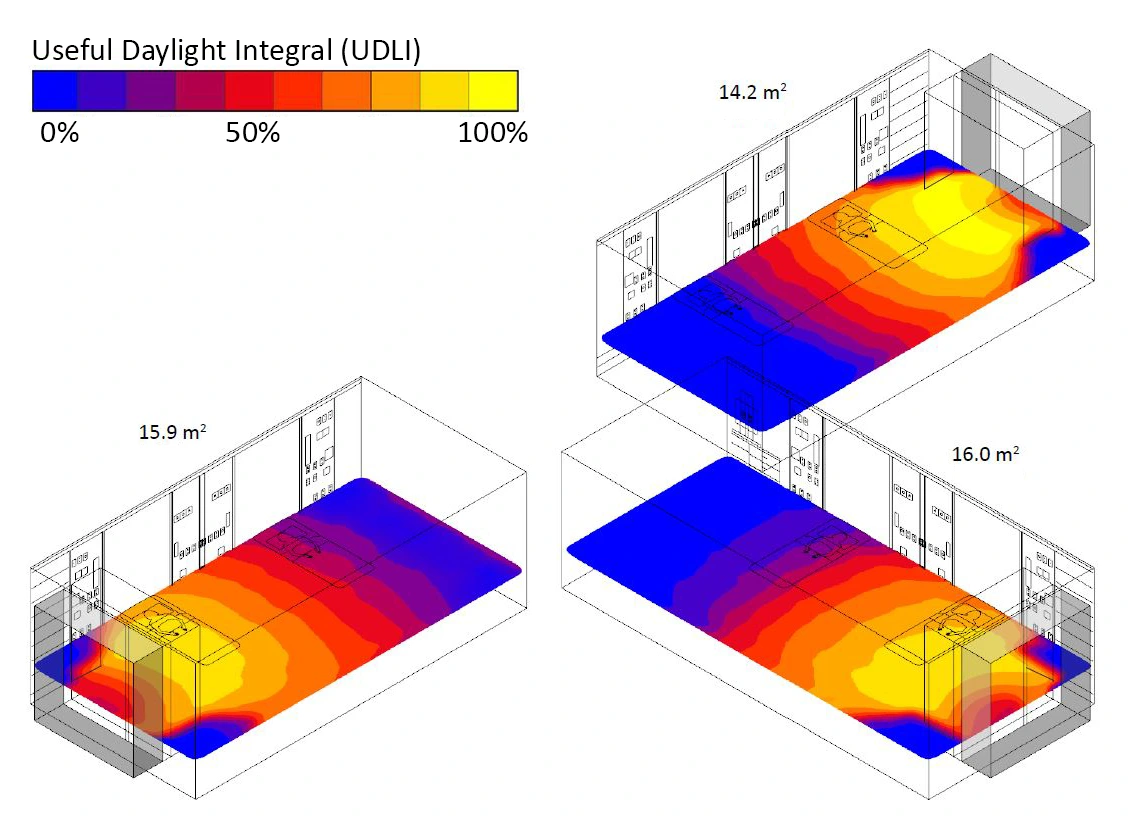
1. Daylight Analysis
By use of daylight analysis, architects may determine the ideal orientation, width, and window location to optimize the natural light flow and minimize obstacles. Well-designed daylighting systems reduce reliance on artificial lighting and improve interior conditions, therefore improving energy economy. During the first design stages, daylight analysis helps to maximize lighting conditions by permitting changes to window width and façade treatments.
LEED Credits on Daylight:
- LEED EQ Credit: Daylight – This credit promotes designs that enhance occupant comfort by providing sufficient daylighting in predominantly occupied areas.
WELL Features on Daylight:
- Feature L03: Circadian Lighting Design – Investigates daylighting alternatives that promote occupant wellness and adhere to the body’s circadian rhythms.
2. Shadow Analysis
The effects of the shadows of the structure and surrounding objects are dedetermined using shadow analysis. This simulation enables builders to create designs that complement their surroundings, therefore reducing the detrimental impact on public spaces and adjacent properties. For city projects, it works particularly effectively as shadow planning doesn’t interfere with the access to light and air of surrounding buildings.
LEED Credits on Shadow Analysis:
- LEED SS Credit: Heat Island Reduction – In order to improve the thermal comfort of outdoor areas and decrease the prevalence of heat islands, shadow analysis could be useful in the design process of shading systems.
WELL Features on Shadow Analysis:
- Feature S05: Solar Glare Control – Enhances passenger comfort and productivity by recognizing and mitigating excessive sun glare concerns.
3. Ray Tracing
Ray tracing models the routes light travels inside the structure to help one understand how reflections and direct sunlight may produce glare. By researching possible glare problems and then designing architectural changes like shifting windows, adding curtains, or utilizing better glazing, architects may provide a more comfortable inside atmosphere. Early ray tracing may be applied to maximize the use of natural light and lower the discomfort generated by glare, therefore optimizing both the exterior and interior designs.
LEED Credits on Ray tracing:
- LEED EQ Credit: Daylight and Views – Effective glare control supports the daylight and views credit by providing access to daylight while minimizing unwanted glare.
WELL Features on Ray tracing:
- Feature S04: Glare Control – Prioritizes designs that manage solar glare through strategic window placement and glazing treatments.
4. Energy Modeling
Using energy models, you can figure out how much energy a building uses by simulating things like lights, HVAC, insulation, and building materials. Later design phases depend on this study to show how environmentally friendly solutions lower the general energy consumption of a building. Energy modeling figures out how much money you can save by using technologies and systems that use less energy. This is in line with the goals of high-performance design.
LEED Credits on Energy Modeling:
- LEED EA Credit: Optimize Energy Performance – In order to qualify for this credit, it is necessary to conduct energy modeling, which evaluates the energy savings that high-performance HVAC systems, insulation, and energy-efficient lighting solutions generate.
WELL Features on Energy Modeling:
- Feature E08: Enhanced Thermal Environment – considers inhabitants’ comfort by guaranteeing ideal energy usage to preserve constant indoor temperature.
5. Thermal Comfort Analysis
Thermal comfort study investigates the impact of various building components, such as insulation, materials, and HVAC systems, on temperature and comfort within a structure. Architects can determine if the building meets occupant comfort standards for temperature and humidity using simulations. This assessment often takes place during the intermediate to latter stages of the design process, while the specifics of the HVAC system are being completed.
LEED Credits on Thermal Comfort:
- LEED EQ Credit: Thermal Comfort – The goal of this credit is to encourage the installation of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems that maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
WELL Features on Thermal Comfort:
- Feature T01: Thermal Environment – Prioritizes maintaining a sufficient temperature to ensure a stable thermal environment.
6. Ventilation and Airflow Analysis
Architects may enhance building ventilation systems by using ventilation and airflow models that assure enough fresh air circulation. Architects may enhance indoor air quality and reduce pollution by utilizing airflow modeling to determine the ideal locations for windows and vents. Accurate airflow modeling is critical in heavily inhabited areas or those with specific ventilation requirements to ensure that indoor air quality meets or exceeds norms.
LEED Credits on Ventilation:
- LEED EQ Credit: Enhanced Indoor Air Quality Strategies – This award is given for the development of ventilation systems that meet very high requirements for air quality.
WELL Features on Ventilation:
- Feature A01: Air Quality Standards – Promotes optimal health and efficiency by emphasizing the need of adequate airflow for maintaining indoor air quality.
7. Water Usage and Rainwater Harvesting Simulation
This model determines if it is possible to collect rainwater and predicts how much water will be used by various construction systems. Architects can save potable water by maximizing water flow and, if feasible, using rainwater for landscape irrigation or greywater systems.
LEED Credits on Water Efficiency:
- LEED WE Credit: Indoor Water Use Reduction – The credits for water efficiency in building operations are based on simulations that educate water consumption plans.
- LEED SS Credit: Rainwater Management – Sustainable site development is made possible by effective on-site rainwater management made possible by accurate projections of rainwater collecting systems.
WELL Features on Water Efficiency:
- Feature W01: Fundamental Water Quality – Efficiently manages and processes water, ensuring its quality and conservation.
8. Acoustic Analysis
In order to create more peaceful and comfortable interior spaces, acoustic simulations examine how sound travels through a structure. Because of the positive effects that reduced noise has on focus and productivity, acoustic comfort is gaining prominence in settings like open offices and schools. In order to guide decisions on materials and layout, this study is carried out at the mid-stage design.
LEED Credits on Acoustic:
- LEED EQ Credit: Acoustic Performance – This credit may be obtained by the utilization of acoustic simulations, ensuring that spaces are designed with adequate soundproofing and acoustic management.
WELL Features on Acoustic:
- Feature S01: Sound Mapping – Manages ambient pollution to foster an environment that is both more conducive to productivity and relaxation.
By focusing on various aspects that contribute to LEED and WELL credits, each of these models assists builders in creating eco-friendly, high-performance structures. By strategically executing simulations, architects may enhance design components, maximize environmental advantages, and create healthier and more efficient interior spaces for occupants.
Firms Known to Use Energy Modeling and Daylight Simulation Softwares
The demand for sustainable design software is directly attributable to the surging interest in green construction practices. To aid projects in achieving LEED and similar certifications, these firms focus or have departments that specialize in energy modeling and daylight simulation. Improving building efficiency, reducing environmental effect, and assuring compliance with green building rules are all made possible by these groups.
Sustainability consulting firms, below are the top 10 environmental consulting companies that use efficient building design software:
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Energy Analysis Software For Architects
Not one piece of architect designing software exists that can be utilized for all kind of simulations. Different design elements are required for every simulation, sunlight analysis, glare management, energy modeling, thermal comfort, etc. The program you use will rely on whether LEED’s emphasis on energy and environmental quality or WELL’s emphasis on human health and comfort fits your project’s sustainable objectives or neither.
By employing appropriate modeling tools and wise design decisions, architects may enhance the health of the people who live or work in a building as well as how well it preserves the surroundings.