Sustainability is not a mere terminology, green building concepts have permeated into the modern world as a promising solution to a holistic lifestyle. Given the pressing challenges imposed by climate change, every sector of the economy is now embracing sustainable building design and green architecture in every facet of work.
Speaking specifically about the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector, professionals have become more sensitive about the impact their work has on the environment. Therefore, sustainable design projects and green building design has emerged as one of the most sought-after ways to achieve sustainability in design and construction.
What is Green Building?
Before we talk about green building concepts, let us first define what a green building is. Most green building councils define a green building as one that amplifies the positive impact, and reduces negative ones, on the environment and enhances the wellbeing of the occupants. Green Architecture have existed long before the talk of sustainability, before green building ratings like LEED and WELL or even before green building councils or organizations were established.
Green building as a concept is holistic, based on the understanding of both the positive and negative impacts on the environment and the occupants. This is vital, especially today, as the industry makes tremendous efforts to amplify the positive impacts while lessening the negative ones throughout the life cycle of a building. A green building, also known as a sustainable or eco-friendly building, is a structure designed and constructed with a focus on minimising its environmental impact throughout its lifecycle.
Sustainable buildings prioritise resource efficiency, energy conservation, and environmentally responsible practices. This involves using sustainable materials, incorporating energy-efficient technologies, optimizing water usage, and promoting a healthy indoor environment. The goal is to reduce the building’s carbon footprint, conserve natural resources, and enhance the overall well-being of occupants.
A green building is one that takes environmental considerations into account throughout the whole building process, from planning to construction to daily maintenance. To that purpose, we use measures like water and energy saving and the use of eco-friendly products. The goal is to reduce a building’s negative effect on the surrounding environment while yet providing a safe and pleasant environment for the people who live or work there.
6 Benefits of Green Architecture
Green building practices are advantageous for the built environment. It aids in the creation of spaces that allow us to thrive while maintaining the ecological balance. Mentioned below are 6 key benefits of green architecture.
1. Energy Efficiency
Green architecture promote energy-efficient design, incorporating features such as advanced insulation, efficient HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources. This not only reduces environmental impact but also leads to significant cost savings for occupants and building owners through lower utility bills.
2. Resource Conservation
Sustainable construction materials, water-efficient systems, and waste-reduction strategies contribute to resource conservation. Green buildings aim to minimize their ecological footprint by responsibly managing resources throughout the building’s lifecycle, from construction to eventual demolition or repurposing.
3. Improved Indoor Air Quality
The concept of green buildings prioritises indoor environmental quality, employing materials and ventilation systems that enhance air quality. This focus on cleaner indoor air contributes to healthier living and working environments, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and allergies for occupants.
4. Reduced Operating Costs
While the initial construction costs for eco-friendly buildings may be higher, the long-term operational savings are substantial. Employing energy-efficient systems, water conservation measures, and reduced maintenance needs contribute to lower operating costs over the building’s lifespan.
5. Enhanced Occupant Well-Being
True sustainable building design seek occupant comfort and well-being. Access to natural light, improved thermal comfort, and ergonomic design contribute to a more pleasant and productive indoor experience. The incorporation of green spaces and biophilic elements further enhances the overall health of occupants.
6. Community Benefits
Green building design often incorporate green spaces such as terrace gardens and green walls that contribute to urban biodiversity. They promote a sense of environmental stewardship while making nature more accessible to the people. Additionally, their focus on local sourcing and job creation during construction fosters community engagement.
7 Green Building Design Techniques
Designing green buildings requires a thorough understanding of the environment and the resources it has to offer. So, while creating sustainable architecture, everything from design conceptualisation to execution has to be done keeping in mind the larger impact of the activity on the site surroundings as a whole. Let’s explore how green building techniques can be applied to building design and construction.
1. Site Analysis and Planning
Understanding the site is a crucial step in determining the overall design and materiality of a project. Consideration of factors like sun exposure, wind patterns, and existing vegetation guides architects in optimizing the building’s relationship with its surroundings.
Resonating with the concept of green buildings, strategic site planning involves harnessing natural features to enhance energy efficiency. This includes aligning structures to maximize solar gain, utilizing prevailing winds for natural ventilation, and preserving existing trees for shading.
2. Energy-Efficient Design
Architects can embrace passive design strategies to minimize reliance on mechanical systems. This involves creating well-insulated building envelopes to regulate indoor temperatures, strategically positioning windows for natural light and ventilation, and incorporating thermal mass to store and release heat.
Furthermore, integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems can also enhance a building’s sustainability. By combining these elements, professionals can significantly reduce energy consumption and contribute to a lower carbon footprint.
3. Environment-friendly Materials
Selecting sustainable materials is integral to the concept of green buildings. Using materials with low environmental impact and favouring the ones that can be locally sourced helps reduce transportation-related emissions. Further, utilizing recycled or repurposed materials can help minimise waste while also promoting a circular economy.
For example, incorporating sustainably harvested wood, recycled steel, and energy-efficient glass ensures that the building materials align with green building principles, supporting both environmental conservation and responsible sourcing.
4. Water Conservation
Integrating water-conserving features, such as low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling aids in efficient water management. Additionally, designing landscapes with native, drought-resistant plants minimizes irrigation needs.
These strategies collectively reduce water consumption, contribute to water conservation efforts, and mitigate the environmental impact associated with traditional water use. In addition to resource conservation, these measures often lead to lower utility costs for building occupants.
5. Indoor Environmental Quality
Prioritizing indoor environmental quality involves designing spaces that promote occupant well-being. Designers can also consider selecting materials with low emissions, providing ample natural light, and ensuring proper ventilation.
Further, incorporating green spaces within the building, such as atriums or living walls can contribute to improved air quality and a connection to nature. These design elements create a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment, positively impacting the physical and mental well-being of occupants.
6. Waste Reduction and Recycling
For the purpose of waste management, professionals must consider minimizing construction and operational waste through strategies such as recycling programs, efficient material usage, and the reuse of materials.
Implementing construction waste management plans can ensure that the waste is diverted from landfills, contributing to a more sustainable construction process. Additionally, designing spaces that encourage recycling and waste reduction practices among occupants promotes a culture of sustainability within the building.
7. Smart Building Technologies
Integrating smart building technologies enhances the operational efficiency of the concept of green buildings. Automated systems for lighting, heating, and cooling can be programmed to adapt to occupancy patterns and external conditions.
For example, sensor-controlled lighting systems can reduce energy consumption by responding to natural light levels or occupancy. Using smart technologies contributes to the dynamic and responsive nature of the building helping optimise resource utilisation.
3 Green building Practices to Design Better
In the quest for a sustainable future, architects and engineers are leveraging cutting-edge technologies to revolutionise the way buildings are conceptualized, designed, and constructed. So, let’s understand how technology is supporting the concept of green buildings and sustainable design projects.
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
BIM has emerged as a cornerstone in green building design, providing a comprehensive digital representation of a structure. Architects utilize BIM to simulate and visualize the environmental impact of a building throughout its lifecycle. BIM enables the integration of sustainable features from the early design stages, facilitating informed decision-making regarding materials, energy efficiency, and overall environmental performance.
2. Parametric Design
Parametric design introduces a dynamic and data-driven approach to architectural creativity. By establishing parameters and algorithms, architects can explore multiple design concepts with real-time analysis of environmental factors. This iterative process allows for the optimisation of building forms, maximising natural light, minimising energy consumption, and enhancing overall sustainability. Parametric design empowers designers to strike an intricate balance between aesthetics and environmental performance.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is reshaping the concept of green buildings by offering predictive analytics and real-time optimization. AI algorithms analyse vast datasets to identify patterns and insights thereby aiding architects in making informed decisions regarding energy consumption, thermal comfort, and material selection. Using AI-driven tools can simulate various scenarios to determine the most environmentally friendly design solutions. This contributes to the creation of energy-efficient and sustainable structures.
What are Green Building Strategies
A green building strategy can cover any design and construction element of the project. It is an actionable strategy that contributes to the green building concept and has a positive environmental impact.
The aim of implementing these strategies in design and construction is to create a decarbonized and sustainable built environment. Some use the term interchangeably with sustainable design strategies; however, it must be emphasized that green building strategies are usually focused on the environmental impact the building may bring.
Discover: Sechelt Water Resource Centre and how it is rethinking traditional municipal wastewater treatment

Green building strategies are occasionally based on vernacular techniques. However, they can also rely on cutting-edge technology, with smart systems for temperature detection and regulation and circular systems. Sometimes, it can be a convergence of high-tech and natural building models. It’s crucial to distinguish genuine strategies from mere symbolic gestures like planting trees without comprehensive considerations. True green building embraces a holistic approach, harmonizing traditional wisdom with innovative solutions for a truly sustainable and efficient built environment.
5 Green Building Strategies
Before we get to the strategies, let us make two things clear. One, be aware of greenwashing – practices that are even barely superficial, yet claim to be sustainable or bring environmental benefits.
Secondly, green building strategies need to be site and context-specific so it is important to understand the surrounding environment, the site and its features. Bear in mind that the type of green building strategy, for example, passive design strategies, and how they are implemented in design will depend on the type of project (or design) and the region. However, we can generally categorize them into common elements.
If you want to see some true green buildings, check out the work of these 15 inspirational sustainable green building architects who are shaping a better built environment.
1. Passive Design Strategies
As a green building strategy, passive design strategies leverage the nature surrounding the site to optimize the design. Rather than installing mechanical and electrical interventions, the design should encourage natural ventilation to cool down the interiors. Implementing passive design strategies brings the occupants closer to nature which in return can boost their wellbeing and productivity. What makes these strategies even more needed is that they lower energy consumption due to less reliance on electrical appliances. A noticeable trend towards passive design strategies has emerged in the past decade as the built environment industry aims for net-zero emissions.
2. Integrating Renewable Energy
By this point, it is not hard to convince any person of the advantages of renewable energy. Adopting it seems entirely different matters for most. We can make a building greener by making use of renewable energy sources (the most commonly available being solar panels) for lighting, heating and cooling purposes. Its reliance on naturally replenishing resources ensures sustainability, contributing to long-term resilience and independence for green buildings. If fossil fuels remain in use, we will have an even unhealthier world full of pollution.
Here is an example of how solar energy can be super efficient – How is the Google Project Sunroof Intelligently Promoting Solar Energy?
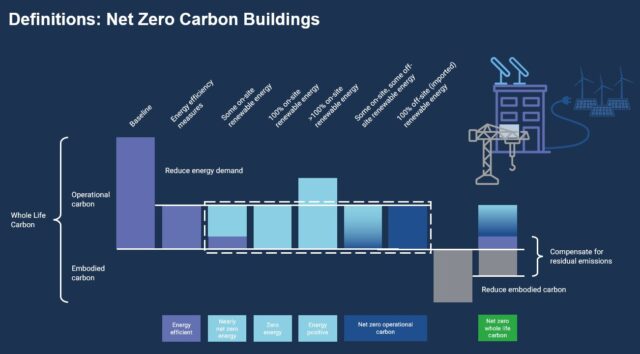
3. Focus On Energy Efficiency
If we can control and mitigate high energy consumption in buildings, we are already on the right path towards sustainability. An energy-efficient building still offers maximum operational efficiency and comfort with the minimum possible energy consumption. This is not only limited to the operation stage of the building’s life cycle; at every stage, stakeholders involved should incorporate measures to ensure energy efficiency.
4. Prioritize The Site And Nature
Every green building strategy is associated closely with nature. The orientation of the building can have a great effect on ventilation and daylighting. If the building is to be naturally ventilated, it is important to orientate the building accordingly to maximize natural ventilation. The same goes for daylighting. The building should be bright and comfortable while reducing heat gain. Any natural features on site such as vegetation should be incorporated into the design as much as possible to sustain them. Manipulating these features to their advantage will create a design that has high efficiency with low energy consumption.
5. Sustainable Materials
Embracing sustainable materials is a pivotal factor in constructing a greener future. It extends beyond mere energy efficiency or looking ‘green’; it is about selecting materials that not only safeguard the environment but also contribute to the well-being of the users. Opting for construction materials that are non-harmful and reduce greenhouse gas emissions is our way of minimizing adverse effects on the site. Preferably, these sustainable materials should also be produced from renewable sources as well as be organic and compostable.
Read more: 10 Best Energy-efficient Building Materials to Construct Sustainable Homes

10 Green Architecture Examples
In a nutshell, environmentally green buildings aim to reduce or eliminate negative impacts on the environment. They also conserve precious resources and enhance our quality of life. There are a number of features that can make a building “green”. These include the efficient use of energy, water, and other resources. Reusability and recycling indoor air quality, use of non-toxic, ethical, sustainable materials and many more.
Any building can be a green building, whether it’s a residential, retail, healthcare, campus, or any other type of structure, as long as it reduces impact. As stated by one of the most well-know green building certifications “LEED” . Now LEED is a title for buildings created by USGBC that acts as a standard for rating systems. There are many others like BREEAM, WELL and Edge. Now even if a project did not target such certifications, it can still be sustainable.
What are examples of top 10 green buildings? Well below you can find 10 of the highest rated sustainable projects of 2022. They top the list with their high performance features, showcasing the benefits of green buildings.
1. The Plus for Vestre by Bjarke Ingels Group
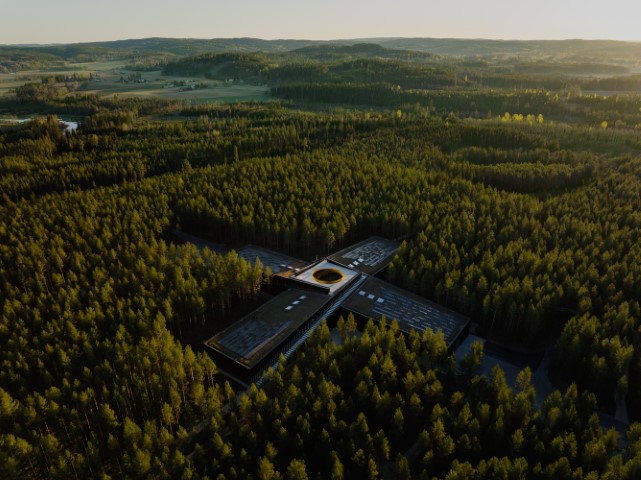

One of the greenest furniture factories in the world. On the path to receiving the highest possible BREEAM grade, “Outstanding.” This green building is presented as a project that is innovative. Speaking of innovation, this enterprise generates 55 percent fewer environmental gases and consumes 60 percent less energy than comparable traditional industries. About 900 photovoltaic panels that produce 250,000 kWh of renewable energy annually are located on the green rooftop. Additionally, 90 to 95 percent of the water utilized in manufacturing will be recycled by the firm. The Plus will meet the Paris Proof goal for energy production on-site and efficiency.
2. Museum of Ethnography Budapest by NAPUR Architect
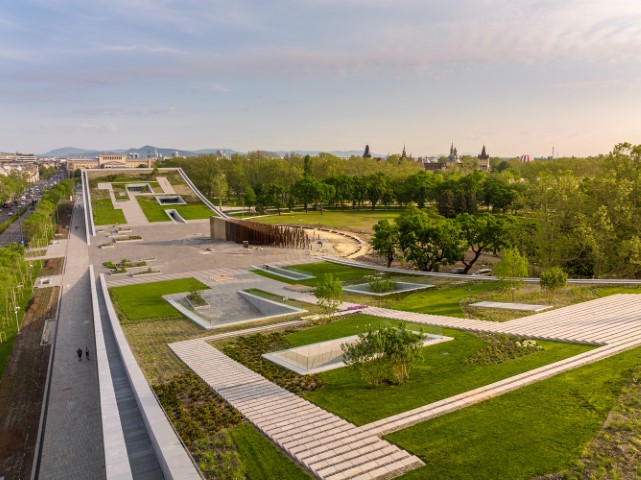

The Liget Budapest Project, the greatest urban-cultural development in Europe, features dynamic yet basic lines that simultaneously blend with the park setting and communicate with the nearby metropolitan area. Standing at the top of our green buildings.
3. Easyhome Huanggang by Stefano Boeri Architetti
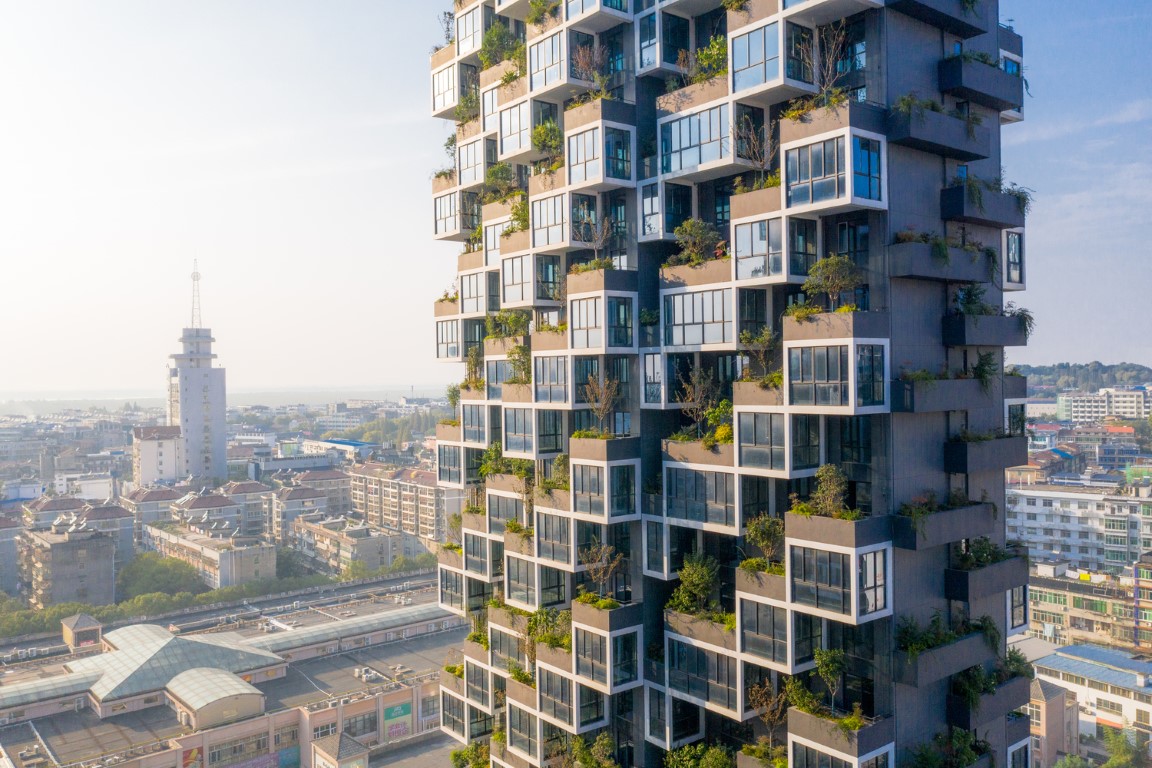

The architect is well known for his vertical forests like the bosco verticale and other green buildings. It’s a brand-new style of Vertical Forests that combines open and closed balconies to break up the regularity of the building and produce a constant, ever-changing movement. The presence of trees and shrubs, which are enabled to grow freely in height by the structure, complements the façade design perfectly.
4. Macha House by Abin Design Studio
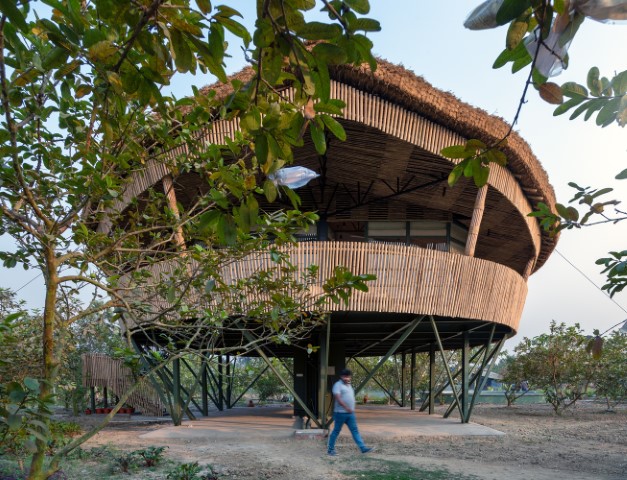

The perimeter of the floor plate is surrounded by livable rooms and patios. The design language is dominated by the delicate weaving of bamboo, which is readily accessible locally and, more significantly, is a material that the locals are familiar with. Metal components are kept to a minimum. The pavilion blends in well with the surroundings thanks to its thatched roof.
5. AUBE Toranomon Residential Building by ETHNOS
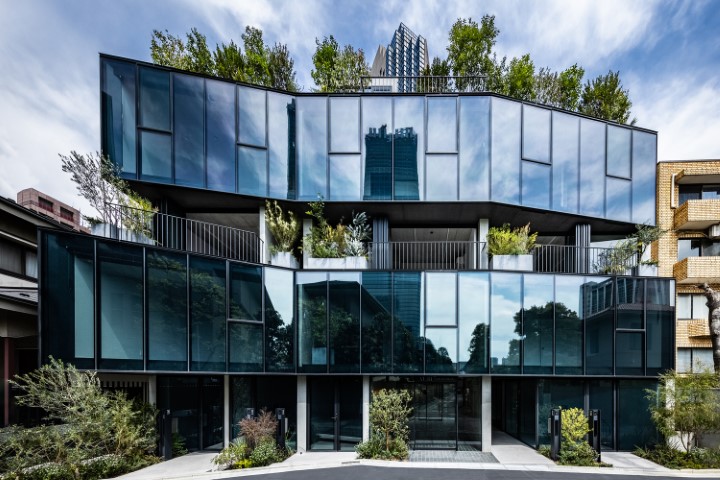

It might not look green but is surely one of the best green buildings ever. The perimeter of the floor plate is surrounded by livable rooms and patios. The design language is dominated by the delicate weaving of bamboo, which is readily accessible locally and, more significantly, is a material that the locals are familiar with. Metal components are kept to a minimum. The pavilion blends in well with the surroundings thanks to its thatched roof.
6. Kakapo Creek Children’s Garden by CASA
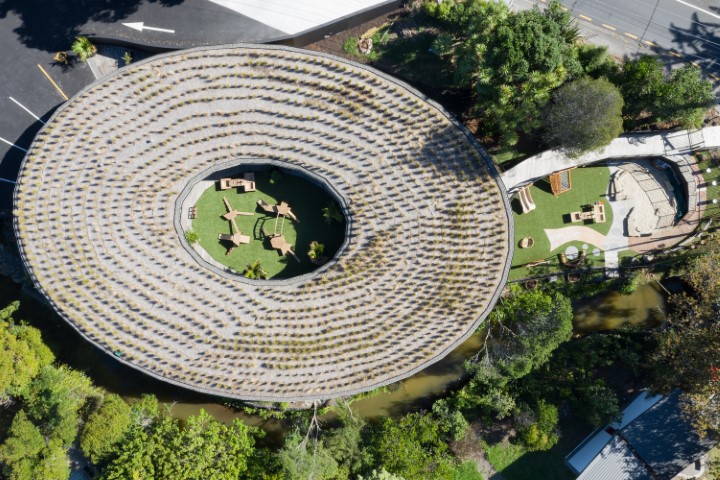

Some of the main environmentally friendly and healthy features include heat pumps that are concealed above the ceilings of bathrooms to offer heating and cooling, which are low-cost to operate and low-carbon. Natural ventilation is also given through the glass doors and windows, which is carbon-neutral. The building’s extensive landscaping and the use of native plants on the roof improve biodiversity.
7. The Ellen DeGeneres Campus by MASS Design Group
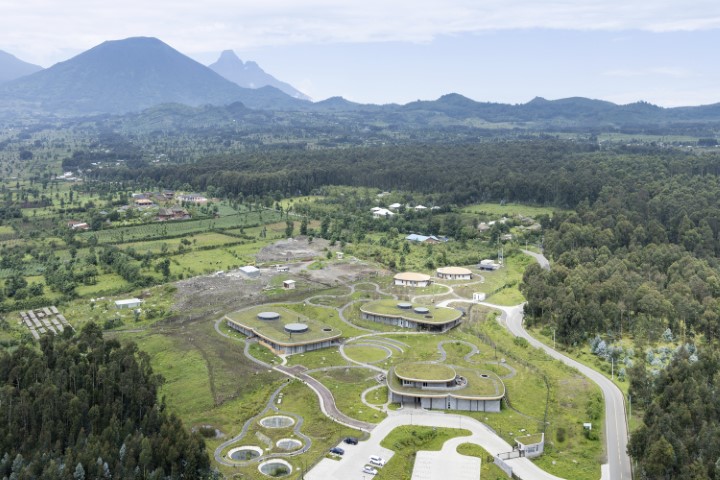

The campus, which is located in Rwanda’s Virunga Mountains, serves as a global benchmark for environmentally friendly architecture and development. The Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund, The Ellen Fund, and MASS Design Group held a ceremony on the site this week to mark the inauguration of the Fossey Gorilla Fund’s The Ellen DeGeneres Campus.
The 12-acre campus serves as a prototype for MASS’s “Purpose-Built” methodology, which weighs and assesses capital infrastructure alongside a project’s goal, design, and viability. Local labor and resources were used throughout the design and construction process to reduce the campus footprint, create an immersive landscape covered in trees, ensure job training and economic benefit to the neighborhood, and build a cutting-edge facility for use by the general public and education.
8. Cage House by ROOM+ Design & Build

Due to a limited budget, a typical little townhouse that is 15 years old and situated in a narrow alleyway in a neighborhood with a high population density recently underwent renovation to meet the demands of the new residents. The outdated home had a hefty concrete staircase in the middle, a cramped kitchen and bedroom at the rear, a dusty rooftop terrace, and a musty, decaying interior. The 3-meter-wide alleyway is usually clogged with bustling, raucous traffic since it serves as a shortcut between two major routes.
9. Sluishuis Residential Building by Bjarke Ingels Group
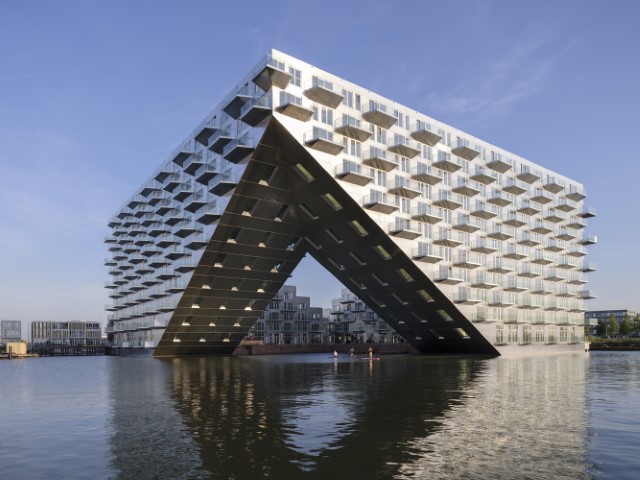

A modern interpretation of the Amsterdam building block type that reacts particularly to its unique setting in the water. The volume is stepped down on the other side to create a welcoming gesture toward IJburg and lifted on one side to let the water enter the courtyard. You hear the Sluishuis loudness differently from every viewpoint. Sluishuis understands how to surprise you from any angle, whether you are standing on a dike, highway, or bridge, crossing jetties or a public path over the roof, or even observing the structure from the air.
10. Orange Village by Koffi & Diabaté Architectes
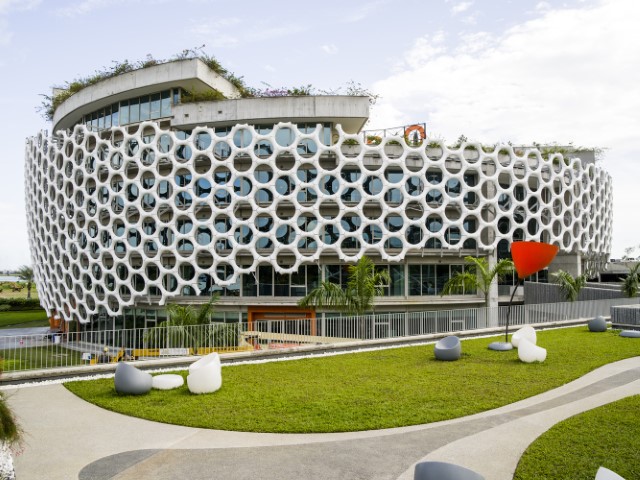

An imposing structure with futuristic style on 7 stories in the shape of rings with a 68 meter circumference using a sustainable architectural method. The unusual design of the new Orange Côte d’Ivoire headquarters, which is reminiscent of a golf ball and subtly evokes Abidjan’s famed Riviera golf course, features a double skin that serves both thermal and aesthetic purposes.
In Conclusion
As the world increasingly recognizes the urgency of mitigating climate change and fostering sustainable practices, the concept of green buildings emerges as a cornerstone in shaping the built environment. It pushes architects, engineers, and construction professionals to create a healthier, more sustainable, and harmonious coexistence with the planet through meaningful design.





