Energy efficient building materials have become essential for mankind. An increase in climate change has alarmed the global population to be more mindful of how their actions are impacting nature. Every sector of the economy is shifting its modus operandi towards a more sustainable approach of ideation, production, and distribution. Speaking of building an energy efficient home, professionals are now making an effort to “think green.” Sustainable design and energy efficient construction practices are gaining prevalence through the incorporation of energy efficient building materials, passive design strategies, and the use of renewable energy.
What are Energy Efficient Buildings?
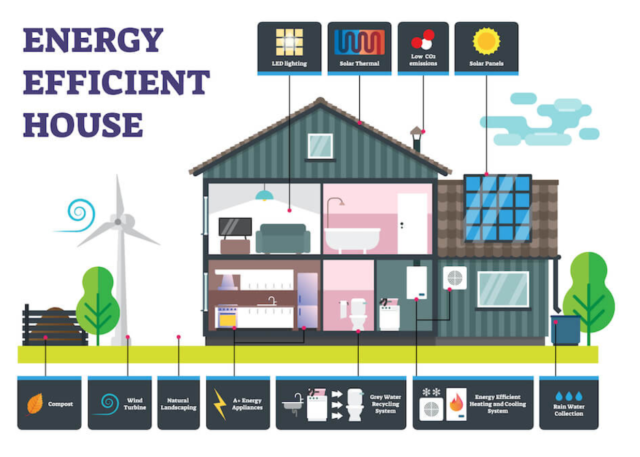
Energy efficient buildings are designed and built with a primary focus on minimizing energy consumption and reducing environmental impact. These projects employ features such as thermal insulation, use of natural resources, renewable energy, energy efficient construction and appliances to reduce their carbon footprint. Homes like these are often built using sustainable house materials that are locally available, environmentally-pally and economical. This helps in creating comfortable indoor spaces while reducing energy bills and greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy Efficiency in Buildings
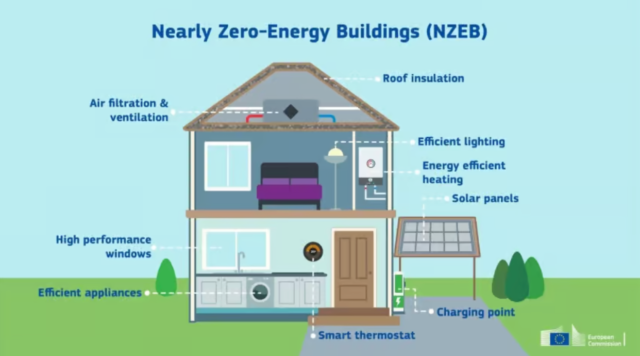
The numbers mentioned below signify how achieving energy efficiency in buildings.
- According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, residential buildings in the United States account for about 21% of the total energy consumed, with the majority used for heating, cooling, and lighting.
- The International Energy Agency states that the global demand for energy is expected to grow by 50% or more by 2050, making energy efficiency crucial for meeting this demand sustainably.
- A survey by Energy Star mentions that energy-efficient homes can save homeowners an average of 30% on energy bills, which can amount to hundreds of dollars annually.
Read: What is the E Star rating system and how it works?
5 Key Benefits of Using Efficient Building Materials

Using energy-efficient building materials enhances the relationship between the built and unbuilt environment. Through textures, colours, and patterns; the building materials converse with their surroundings and aid the creation of engaging spaces. Let’s have a look at how the use of sustainable materials proves beneficial for energy-efficient homes.
Reduced Energy Consumption
The most significant benefit of using sustainable house materials is the considerable reduction in energy consumption. These materials are designed to enhance insulation and reduce heat transfer, effectively minimising the need for heating and cooling systems. For instance, high-quality insulation materials and windows with low emissivity coatings can help maintain consistent indoor temperatures. This means less reliance on heating in the winter and air conditioning in the summer, resulting in lower energy bills for homeowners.
Lower Operating Costs
Energy efficient building may have a slightly higher upfront cost, but they pay off over the long run. The reduced energy consumption leads to lower monthly utility bills, which can result in substantial savings over the life of a building. In commercial settings, lower operating costs can make businesses more competitive, while in residential properties, homeowners enjoy increased disposable income due to reduced energy expenses. The initial investment in building energy efficiency is thus quickly recouped.
Enhanced Comfort
The use of sustainable materials contributes to improved indoor comfort. Proper insulation and materials that regulate temperature effectively create more stable indoor environments. This means fewer drafts, fewer temperature fluctuations, and a more comfortable living or working space. Additionally, the use of energy-efficient windows often reduces noise pollution, further enhancing the quality of life for occupants.
Extended Lifespan
Most architects and engineers select energy-efficient building materials and are often chosen for their durability. These sustainable house materials are engineered to withstand numerous environmental conditions and maintain their performance over time. When you invest in sustainable materials, you’re not only improving energy efficiency in buildings but also increasing the lifespan. This longevity translates into fewer replacements and less maintenance, saving both time and money in the long term.
Environmental Sustainability
The most compelling benefit of using energy efficient materials is their positive impact on the environment. These materials help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by lowering energy consumption. In addition, many energy-efficient building materials are made from sustainable or recycled sources, further reducing their environmental footprint. By choosing such materials, you’re contributing to the reduction of carbon emissions and the conservation of valuable resources.
How to Select Energy-Efficient Building Materials for Building Your Home?
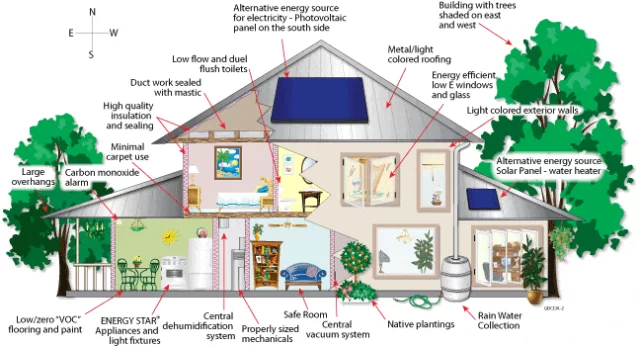
Building an energy efficient house is a wise investment for your future, your comfort, and the environment. Here is how you can select sustainable house materials.
Set Clear Energy Efficient Building Goals
Before diving into energy saving materials, define your energy efficiency goals. Consider factors such as your budget, climate, and sustainability preferences. Determine the level of energy efficiency you want to achieve, whether it’s meeting basic standards or striving for a net-zero energy home. Identifying your purpose will guide your material choices effectively.
Insulation is Key
Insulation is the foundation of energy efficient construction. Look for high-performance insulation materials such as fibreglass, cellulose, spray foam, and rigid foam boards with a high R-value (thermal resistance). Ensure that the insulation material is properly installed to minimise gaps and air leaks, as these can lead to energy losses.
Prioritise Recycled Materials
Embrace sustainability by opting for energy-efficient building materials made from recycled or renewable resources. Seek out options like reclaimed wood, bamboo flooring, and recycled steel. Such materials often have lower environmental footprints and contribute to a greener building industry.
Opt for Low-VOC Finishes
For paints, adhesives, sealants, and finishes, opt for materials and products with low volatile organic compound (VOC) content. These low-VOC products release fewer harmful chemicals into indoor air, contributing to better air quality. This helps in creating healthier spaces where people feel comfortable.
Consider Environmental Certifications
Look for building materials that carry environmental certifications, such as Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification for wood products or Cradle to Cradle certification for various other materials. These certifications indicate that the materials meet stringent environmental and sustainability criteria making them suitable for use in energy-efficient homes.
Top 10 Energy-Efficient Building Design
In today’s environmentally conscious world, the construction industry is rapidly embracing energy-efficient building materials that not only reduce the ecological footprint but also enhance building performance. Mentioned-below are the most widely-used sustainable materials for constructing homes.
1. Rammed Earth
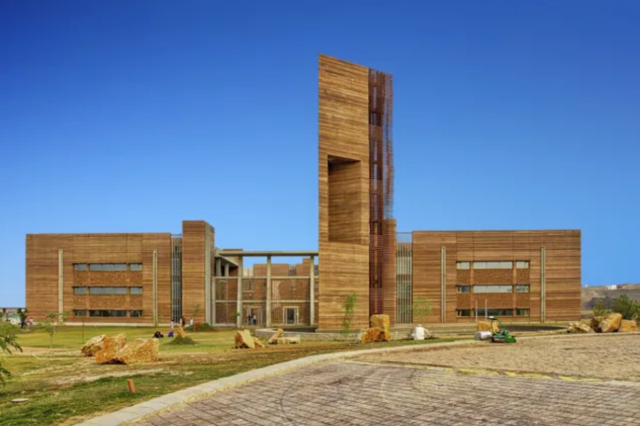

Rammed earth, an ancient building technique, involves compressing layers of earth or soil to create sturdy, load-bearing walls. The process begins by layering moistened earth, which is then compressed using manual or mechanical methods. This building for energy efficiency is a solid, durable wall with exceptional thermal mass properties.
Rammed earth walls are an energy-efficient building material as they have the unique ability to absorb and slowly release heat, effectively regulating indoor temperatures. This natural insulation reduces reliance on mechanical heating and cooling systems, resulting in considerable building energy efficiency. Additionally, rammed earth buildings are renowned for their longevity and low maintenance requirements, making them a sustainable choice that stands the test of time.
2. Hempcrete

Hempcrete is a bio-composite material made from hemp fibres mixed with lime and water. This material is lightweight, strong, and possesses exceptional insulation properties. Hemp fibres are mixed with lime and water to create a versatile construction material that can be used for walls, floors, and roofs.
Hempcrete naturally regulates humidity levels within a building, contributing to a comfortable living environment. Its excellent thermal insulation abilities reduce the energy required for climate control. Hempcrete is also a carbon-negative material, sequestering carbon dioxide during its production and further enhancing its sustainability credentials. The cultivation of hemp itself is eco-friendly, requiring minimal water, pesticides, and synthetic fertilisers, making hempcrete a truly green building choice.
3. Strawbale
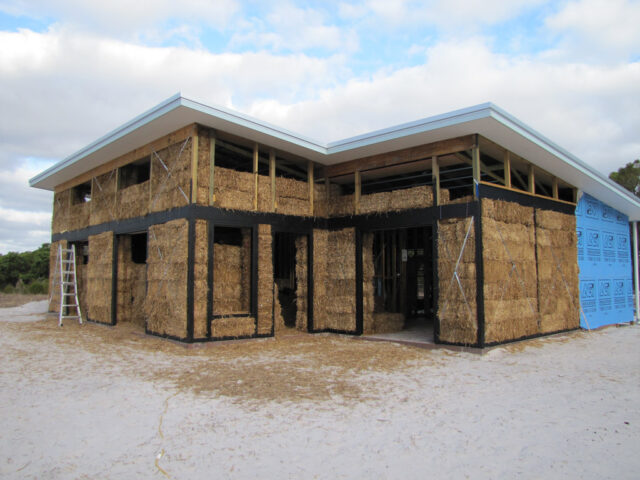

Strawbale construction employs straw bales as building blocks, often covered with plaster for protection. Straw as an energy-efficient building material is a superb natural insulator, offering superior thermal performance. Homes constructed with strawbale provide excellent insulation, leading to reduced energy consumption for both heating and cooling throughout the year.
Strawbale structures are known as energy saving materials and can maintain comfortable indoor temperatures with minimal heating or cooling. These buildings also boast impressive fire resistance, soundproofing qualities, and a reduced carbon footprint due to the sustainable nature of straw as a building material. Additionally, strawbale is typically used when targeting energy efficient construction. Utilizing locally sourced materials, reducing transportation-related emissions and supporting local economies.
4. Bamboo
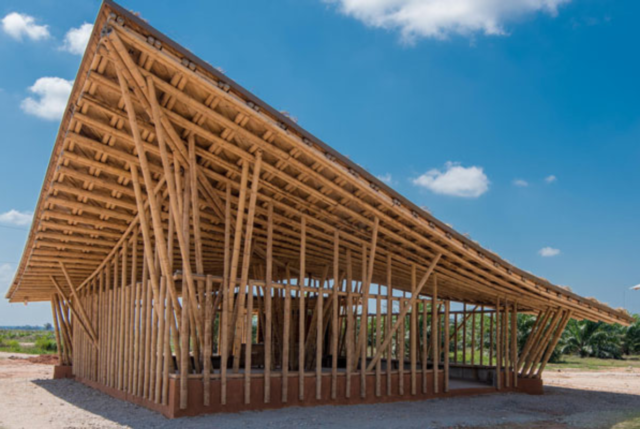

Bamboo is a rapidly renewable grass that has gained recognition as an energy-efficient building material. Due to its quick growth, bamboo reduces the strain on forests and contributes to forest preservation. It possesses impressive strength and durability, making it a reliable choice for structural elements in construction.
Beyond its structural qualities, bamboo’s insulation properties are noteworthy. It acts as an organic insulator, helping maintain stable indoor temperatures and reducing the energy required for heating and cooling. Bamboo is a testament to nature’s capacity to provide sustainable materials for the built environment, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious architects and builders.
5. Cork
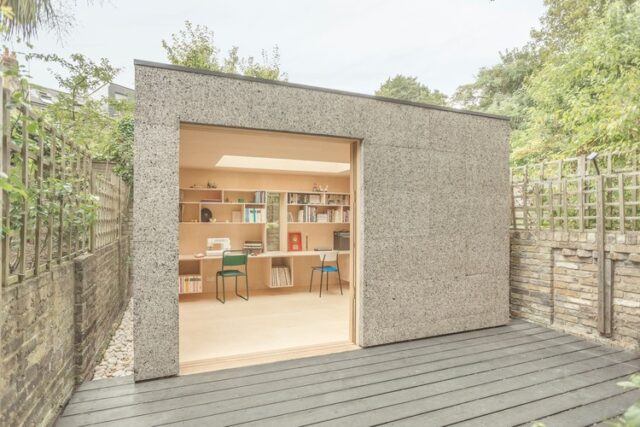

Cork is harvested from cork oak trees and finds its place in construction as insulation or a component of composite materials. As a natural insulator, cork boasts low thermal conductivity, which reduces heat transfer and assists in keeping indoor temperatures stable. This not only enhances energy efficient building design but also lessens the demand for energy-intensive heating and cooling systems.
Cork’s sustainable harvesting methods are particularly environmentally friendly. The process doesn’t harm the cork oak tree, allowing it to continue absorbing carbon dioxide, thus making cork an eco-conscious choice for builders committed to reducing their environmental impact.
6. Recycled Steel
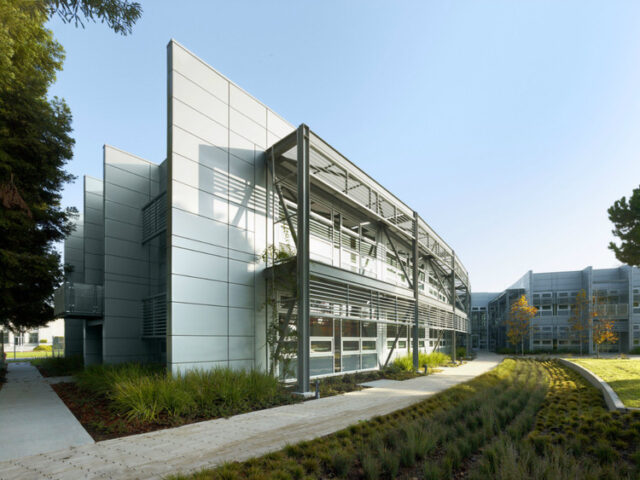

Recycled steel, often used for structural elements, is manufactured from steel scrap. Utilising recycled steel significantly reduces the environmental impact associated with steel production, as it requires fewer resources and energy compared to producing steel from raw materials.
Furthermore, steel’s durability and longevity make it a compelling choice as an energy-efficient building material for large-span structures. It contributes to the overall sustainability of buildings by minimising the need for replacements or maintenance.
7. Reclaimed Wood
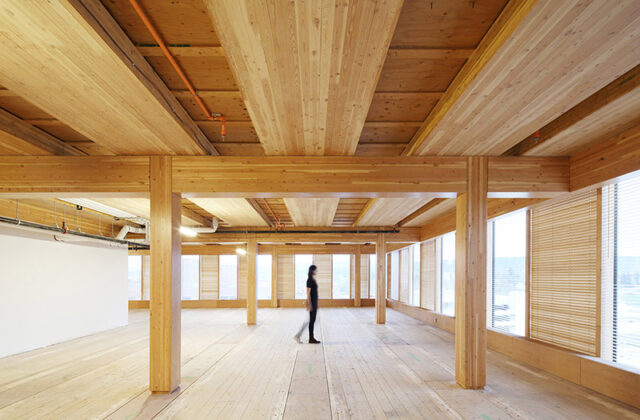

Reclaimed wood is salvaged from old structures and repurposed in modern construction. Beyond its aesthetic appeal and unique character, reclaimed wood offers natural insulation properties. This wood has the ability to regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for additional heating and cooling.
Furthermore, by reusing old wood, builders are diverting materials from landfills and reducing the demand for new timber production. This not only reduces waste but also lessens the carbon footprint associated with harvesting and processing new wood.
8. Low-Emission Glass
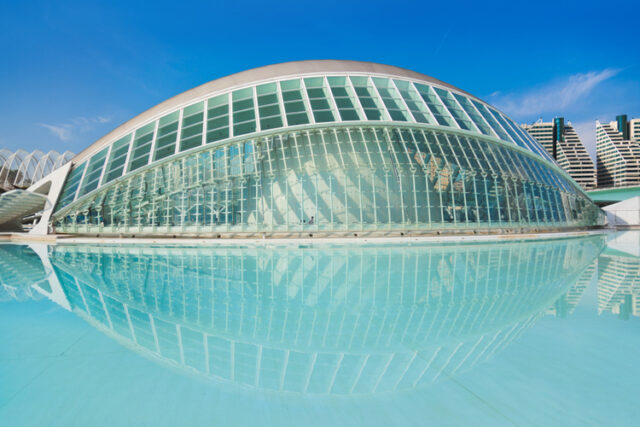

Low-Emission (Low-E) glass is a technological innovation in the realm of windows and glass facades. This glass is treated with a microscopically thin, nearly invisible coating that controls heat flow. Low-E glass enhances the energy performance of windows by reflecting heat while allowing visible light to pass through. to achieve energy efficient building design.
In practice, this means that during hot weather, less heat enters the building, reducing the need for air conditioning. Conversely, during colder months, less heat escapes, diminishing heating demands. Beyond its energy efficiency attributes, Low-E glass supports in building an energy efficient home, providing additional benefits such as reduced UV exposure and fading of interior furnishings, making it an ideal choice for sustainable and energy efficient construction.
9. Wood Composite Lumber
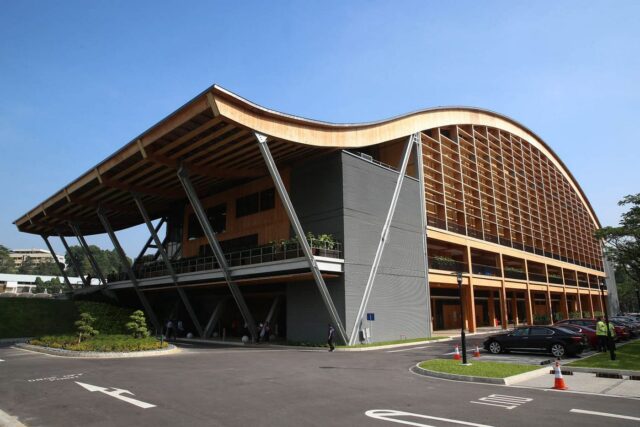

Wood composite lumber as an energy-efficient building material is crafted from recycled wood fibres and plastics, often referred to as composite decking or lumber. This material is gaining popularity as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood. It plays a crucial role in reducing the demand for virgin timber, which helps conserve forests and biodiversity. Additionally, wood composite lumber offers excellent insulation properties, making it an ideal choice for energy-efficient construction.
Its insulating characteristics reduce heat transfer, which, in turn, contributes to maintaining stable indoor temperatures and lowering the need for artificial heating and cooling. Moreover, wood composite lumber is highly resistant to rot, insects, and moisture, ensuring its longevity and minimising maintenance requirements.
10. Insulated Concrete

Insulated concrete represents a dynamic fusion of traditional concrete with insulation materials, typically foam boards, to create walls with exceptional thermal resistance. These walls provide outstanding insulation, minimising heat transfer and maintaining stable indoor temperatures. As a result, insulated concrete structures substantially reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling purposes.
Beyond energy saving materials, insulated concrete offers durability and resilience, reducing the need for ongoing maintenance and repairs. This long-lasting quality not only saves resources but also minimises the overall environmental footprint associated with building maintenance. Insulated concrete is particularly beneficial in regions with extreme temperature fluctuations, where it ensures comfortable and energy-efficient living conditions.
In Conclusion
“As the saying goes, the Stone Age did not end because we ran out of stones; we transitioned to better solutions. The same opportunity lies before us with energy efficiency and clean energy,” said Steven Chu, a notable American physicist. The time to go sustainable is now and so, we must act upon our instincts of being responsible towards the environment. As we continue to advance in our understanding of sustainable construction, embracing the energy-efficient building materials mentioned above not only enhances the quality of our living spaces but also contributes to a more ecologically balanced and harmonious future.





